A healthy lifestyle can prevent progression or lessen the burden of Afib.

AFIB classification:
Stage 1 (at risk for Afib): presence of risk factors such as obesity, hypertension, sleep apnea, genetics, and older age
Stage 2 (pre-Afib): evidence of structural or electrical findings such as atrial enlargement and atrial flutter
Stage 3 (Afib): substages from paroxysmal Afib , persistent Afib , and long-standing persistent Afib, to successful Afib ablation
Stage 4 (permanent Afib): no further attempts at rhythm control or monitoring following a patient-clinician discussion.
Across all four stages in Afib, modifiable risk factors should be treated, whether with lifestyle changes or medications. A healthy lifestyle can prevent progression or lessen the burden of Afib. Obese and overweight patients should target 10% weight loss. People with Afib should perform 210 minutes of weekly moderate-to-vigorous exercise. Also recommended were tobacco cessation for smokers and reduced alcohol consumption in people with Afib.
In contrast, abstaining from caffeine was deemed to be of no benefit in Afib, though it may reduce symptoms in patients reporting caffeine as a trigger for Afib symptoms.
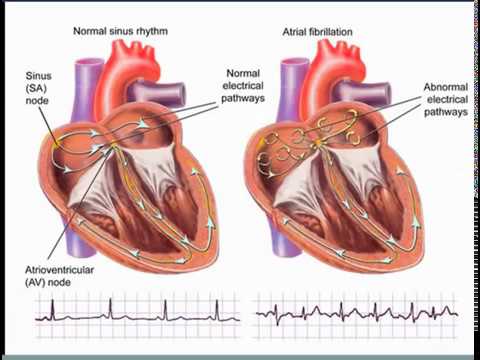
“This is a complex disease. It’s not just an isolated disorder of the heart’s rhythm, and we now know that the longer someone is in Afib, the harder it is to get them back to normal sinus rhythm,” said Jose Joglar, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.